

More information about communities, support for multiple supernodes, routing, traffic restrictions and on how to run an edge asĪ service is available in the more detailed documentation. Hostname and the community name optionally can be encrypted applying -H on the edges. The header which contains some metadata like the virtual MAC address of the edge nodes, their IP address, their real Other ciphers can be chosen using the -A_ option.Ī benchmark of the encryption methods is available when compiled from source with tools/n2n-benchmark. n2n edge nodes useĪES encryption by default. Please haveĪ look at Crypto description for a quick comparison chart to help make a choice. The choice of encryption schemes that can be applied to payload has recently been enhanced. The traffic exchanged between two edge nodes but it will know that edge A is talking with edge B.

When payload encryption is enabled (provide a key using -k), the supernode will not be able to decrypt Feedback in the Issues section is appreciated. On the other hand, if you dare to try bleeding edge features, you are encouraged to compile from dev – just keep track of sometimes rapidly occuring changes. Please note that the current dev branch usually is not guaranteed to be backward compatible neither with the latest stable release nor with previous dev states.
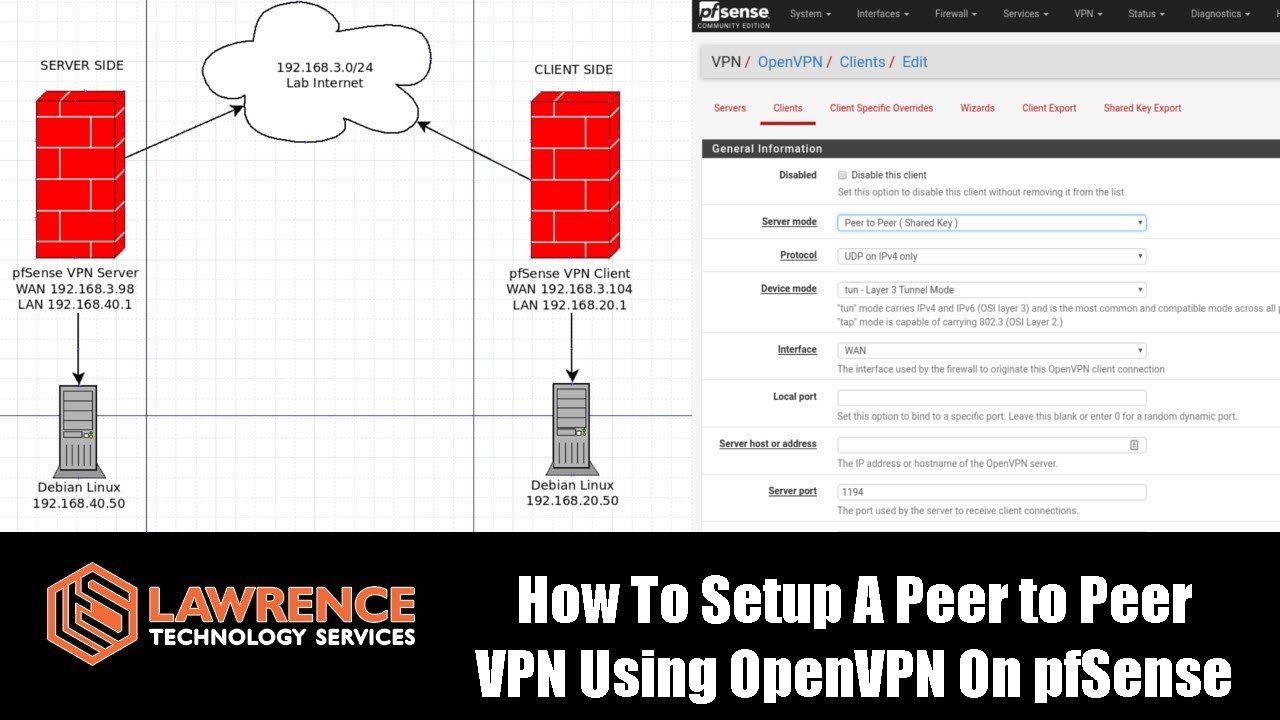
IMPORTANT It is generally recommended to use the latest stable release. Alternatively, up-to-date packages for most distributions are available on ntop repositories.įor Windows, MacOS, optimizations and general building options, please check out Building documentation for compilation and running. Some Linux distributions already provide n2n as a package so a simple sudo apt install n2n will do the work. When this is not possible (usually due to special NAT devices), the supernode is also used to relay the packets. N2n tries to establish a direct peer-to-peer connection via udp between the edge nodes when possible. An encryption key can be used by the edge nodes to encrypt the packets within their community. A single supernode can relay multiple communities and a single computer can be part of multiple communities at the same time.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
